EDIT based on comments/ suggeestions from @JonoCarroll Disqus profile and @tjmahr twitter profile. See below (last step; look for “EDIT”).
Thanks for the input! ![]()
reading time: 10 min.
Hadley Wickham’s purrr has given a new look at handling data structures to the typical R user (some reasoning suggests that average users doesn’t exist, but that’s a different story).
I just tried the following with purrr:
- Meditate about the running a simple regression, FWIW
- Take a dataframe with candidate predictors and an outcome
- Throw one predictor at a time into the regression, where the outcome variable remains the same (i.,e multiple simple regressions (one predictor) where the predictor is changed at each run but the outcome remains the same)
- tidy up the resulting $R^2$ in some nice format
I found that purrr does the job nicely, and it’s quite instructive to see purrrat work, I think. That’s why I wrote it up in this short post:
library(purrr)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(broom)
library(knitr) # for kable
data(Fair, package = "Ecdat") # extramarital affairs dataset
glimpse(Fair)
## Observations: 601
## Variables: 9
## $ sex <fctr> male, female, female, male, male, female, female, ...
## $ age <dbl> 37, 27, 32, 57, 22, 32, 22, 57, 32, 22, 37, 27, 47,...
## $ ym <dbl> 10.00, 4.00, 15.00, 15.00, 0.75, 1.50, 0.75, 15.00,...
## $ child <fctr> no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, yes, no, yes, y...
## $ religious <int> 3, 4, 1, 5, 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 4, 2, 4, 5, 2, 4, 1, 2, ...
## $ education <dbl> 18, 14, 12, 18, 17, 17, 12, 14, 16, 14, 20, 18, 17,...
## $ occupation <int> 7, 6, 1, 6, 6, 5, 1, 4, 1, 4, 7, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 4, ...
## $ rate <int> 4, 4, 4, 5, 3, 5, 3, 4, 2, 5, 2, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 3, ...
## $ nbaffairs <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, ...
Fair %>%
dplyr::select(-nbaffairs) %>% # exclude outcome, leave only predictors
map(~lm(Fair$nbaffairs ~ .x, data = Fair)) %>%
map(summary) %>%
map_dbl("r.squared") %>%
tidy %>%
dplyr::arrange(desc(x)) %>%
rename(r.squared = x) -> r2s
kable(r2s)
| names | r.squared |
|---|---|
| rate | 0.0781272 |
| ym | 0.0349098 |
| religious | 0.0208806 |
| child | 0.0108181 |
| age | 0.0090701 |
| occupation | 0.0024613 |
| sex | 0.0001377 |
| education | 0.0000059 |
Ok, that appears to be the list of the $R^2$ for each simple (one-predictor) regression we have run.
Let’s do a quick sense check with the standard way:
lm1 <- lm(nbaffairs ~ rate, data = Fair)
summary(lm1)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = nbaffairs ~ rate, data = Fair)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -3.9063 -1.3989 -0.5631 -0.5631 11.4369
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 4.7421 0.4790 9.900 <2e-16 ***
## rate -0.8358 0.1173 -7.125 3e-12 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 3.17 on 599 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.07813, Adjusted R-squared: 0.07659
## F-statistic: 50.76 on 1 and 599 DF, p-value: 3.002e-12
summary(lm1)$r.squared
## [1] 0.07812718
summary(lm1)$coefficients[2, 4] #p.value
## [1] 3.002385e-12
Seems to work. To get details of the object summary(lm1), use str(summary(lm1)).
How many did we run? Just the number of columns minus one (the outcome variable).
ncol(Fair)-1
## [1] 8
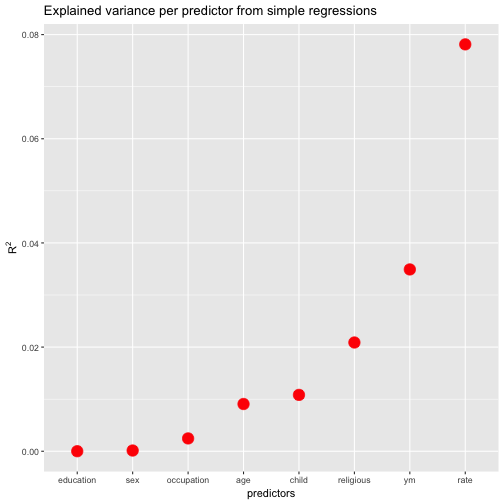
FWIW, let’s plot the resulting values (and sort the predictors by descending values).
ggplot(r2s, aes(x = reorder(names, r.squared), y = r.squared)) +
geom_point(size = 5, color = "red") +
ylab(expression(R^{2})) +
xlab("predictors") +
ggtitle("Explained variance per predictor from simple regressions")
Wait, one more thing. Suppose we are not only interested in \(R^2\), but in the p-values (OMG). How to get both values from purrr?.
EDIT (the following part has changed)
Thanks for comments from @JonoCarroll Disqus profile and @tjmahr twitter profile, the last step - extracting the p-values - is now changed, and I think improved.
Fair %>%
dplyr::select(-nbaffairs) %>% # exclude outcome, leave only predictors
map(~lm(Fair$nbaffairs ~ .x, data = Fair)) %>%
map(summary) %>%
map(broom::tidy) %>%
map_df("p.value") %>%
round(3) %>%
mutate(variable = c("intercept", "predictor")) -> ps
library(htmlTable)
htmlTable(ps)
| sex | age | ym | child | religious | education | occupation | rate | variable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.465 | 0.019 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.002 | 0 | intercept |
| 2 | 0.774 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.011 | 0 | 0.952 | 0.225 | 0 | predictor |
So what I did above basically is:
- Run a linear model on each predictor
- Get a
summaryof each model - Tidy (with
broom) each summary - Get the sublist (column)
p.valuefrom each list (model), and save the result as a data frame
To get a whole bunch of relevant statistics, you can use glance:
Fair %>%
dplyr::select(-nbaffairs) %>% # exclude outcome, leave only predictors
map( ~lm(Fair$nbaffairs ~ .x, data = Fair)) %>%
map(summary) %>%
map_df(glance) %>%
round(3)
## r.squared adj.r.squared sigma statistic p.value df
## 1 0.000 -0.002 3.301 0.083 0.774 2
## 2 0.009 0.007 3.287 5.483 0.020 2
## 3 0.035 0.033 3.243 21.667 0.000 2
## 4 0.011 0.009 3.284 6.551 0.011 2
## 5 0.021 0.019 3.267 12.774 0.000 2
## 6 0.000 -0.002 3.302 0.004 0.952 2
## 7 0.002 0.001 3.297 1.478 0.225 2
## 8 0.078 0.077 3.170 50.764 0.000 2
Thanks for comments from @JonoCarroll Disqus profile and @tjmahr twitter profile, the last step - extracting the p-values - is now changed, and I think improved.