library(rstanarm)
library(tidyverse)
library(easystats)
diamonds_path <- "https://vincentarelbundock.github.io/Rdatasets/csv/ggplot2/diamonds.csv"
d <- data_read(diamonds_path)diamonds-nullhyp-mws
Exercise
Betrachten Sie folgende Ausgabe eines Bayesmodells, das mit rstanarm “gefittet” wurde:
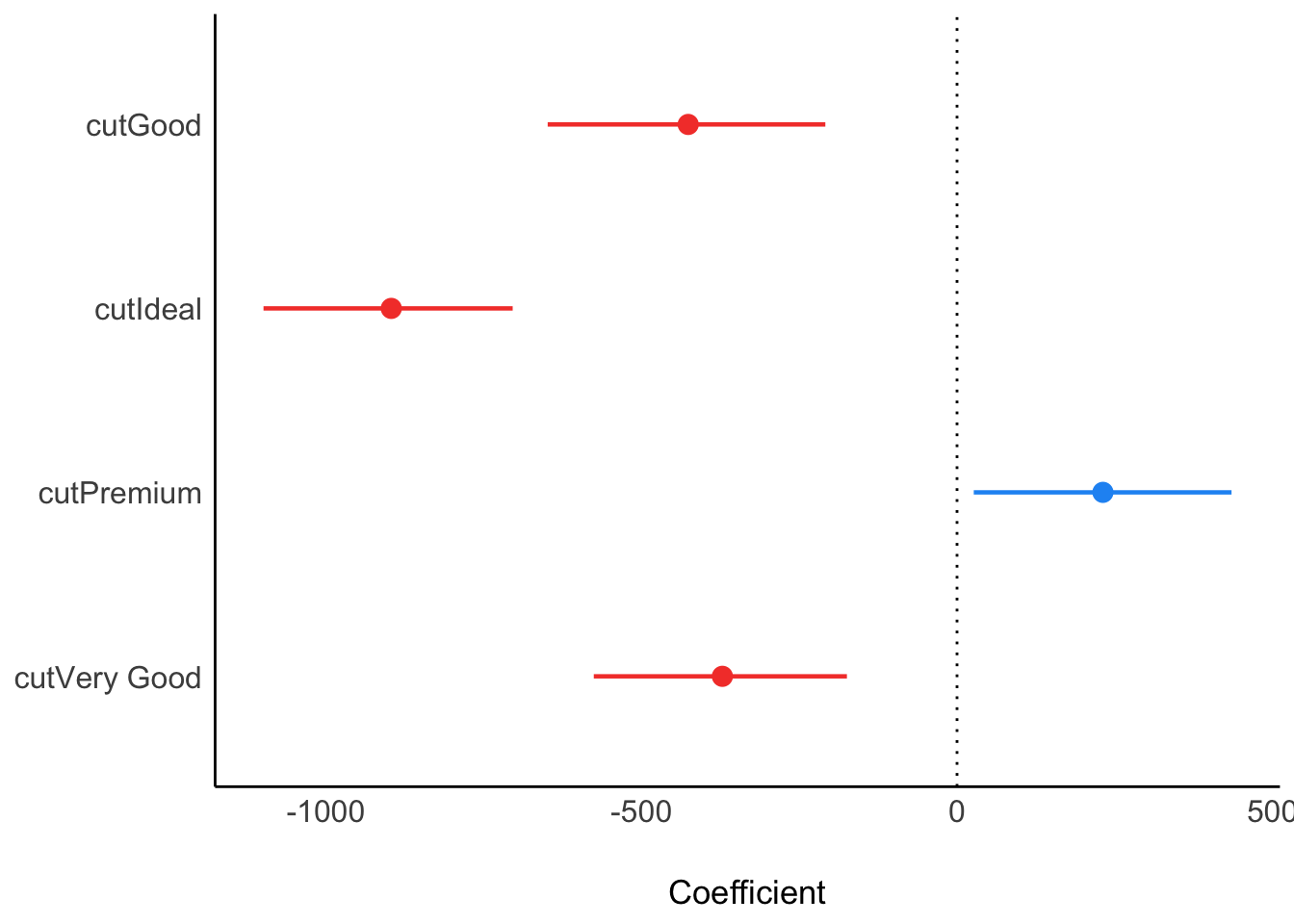
Parameter | Median | 95% CI | pd | Rhat | ESS | Prior
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | 4354.87 | [ 4169.07, 4547.04] | 100% | 1.001 | 1217.00 | Normal (3932.80 +- 9973.60)
cutGood | -426.02 | [ -648.68, -208.69] | 100% | 1.001 | 1425.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 34685.38)
cutIdeal | -896.54 | [-1099.03, -704.16] | 100% | 1.001 | 1239.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 20362.28)
cutPremium | 231.20 | [ 26.53, 435.01] | 98.75% | 1.001 | 1292.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 22862.49)
cutVery Good | -371.85 | [ -575.61, -174.49] | 100% | 1.001 | 1237.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 23922.15)Aufgabe:
Welche der folgenden Aussage passt (am besten)?
Hinweise:
- Mit “Nullhypothese” ist im Folgenden dieser Ausdruck gemeint: \(\mu_1 = \mu_2 = \ldots = \mu_k\).
- Gehen Sie davon aus, dass die Posteriori-Verteilungen der Regressionskoeffizienten normalverteilt sind.
- Beziehen Sie sich bei den Antworten auf die oben dargestellten Daten.
Answerlist
- Die Nullhypothese ist (sicher) falsch.
- Die Nullhypothese ist (sicher) wahr.
- Man kann schließen, dass beim Parameter von
cutGoodder Wert Null außerhalb des 95%-PI der Posteriori-Verteilung liegt. - Man kann schließen, dass alle Parameter positiv sind.
Solution
Probieren geht über Studieren:
m1 <- stan_glm(price ~ cut,
seed = 42,
refresh = 0,
data = d)| Parameter | Median | 95% CI | pd | Rhat | ESS | Prior |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 4357.10 | (4163.48, 4549.00) | 100% | 1.002 | 1306 | Normal (3932.80 +- 9973.60) |
| cutGood | -427.20 | (-648.34, -204.05) | 100% | 1.002 | 1417 | Normal (0.00 +- 34685.38) |
| cutIdeal | -898.81 | (-1099.14, -701.90) | 100% | 1.002 | 1313 | Normal (0.00 +- 20362.28) |
| cutPremium | 227.09 | (24.00, 430.03) | 98.67% | 1.002 | 1283 | Normal (0.00 +- 22862.49) |
| cutVery Good | -376.00 | (-578.22, -171.87) | 100% | 1.002 | 1387 | Normal (0.00 +- 23922.15) |
Anmerkungen:
Streng logisch betrachtet ist die Aussage ” Die Nullhypothese ist sicher falsch” und “Die Nullhypothese ist falsch” in diesem Kontext vermutlich gleichwertig. Würde man aber sagen: “Auf Basis der Datenlage ist die Nullhypothese zu verwerfen”, wäre der Aussage zuzustimmen. Postuliert eine Nulllhypothese die Gleichheit von z.B. 5 Werten, so ist die Hypothese schon dann falsifiziert, wenn sich nur ein Wert von den anderen (vieren) unterscheidet. Wir verstehen dabei unter “unterscheidet” sich, dass sich die Null nicht im 95%-KI des Unterschieds zwischen zwei Werten befindet.
Answerlist
- Falsch. Streng genommen können wir nicht ganz sicher sein, ob eine Hypothese auf Basis eines Modells richtig oder falsch ist.
- Falsch. Streng genommen können wir nicht ganz sicher sein, ob eine Hypothese auf Basis eines Modells richtig oder falsch ist.
- Richtig. Das 95%-ETI enthält die Null nicht; die Null liegt außerhalb des Intervalls.
- Falsch.
cutGoodhat z.B. negative Werte in seinem 95%-ETI der Postverteilung.
Categories:
- bayes
- regression
- null